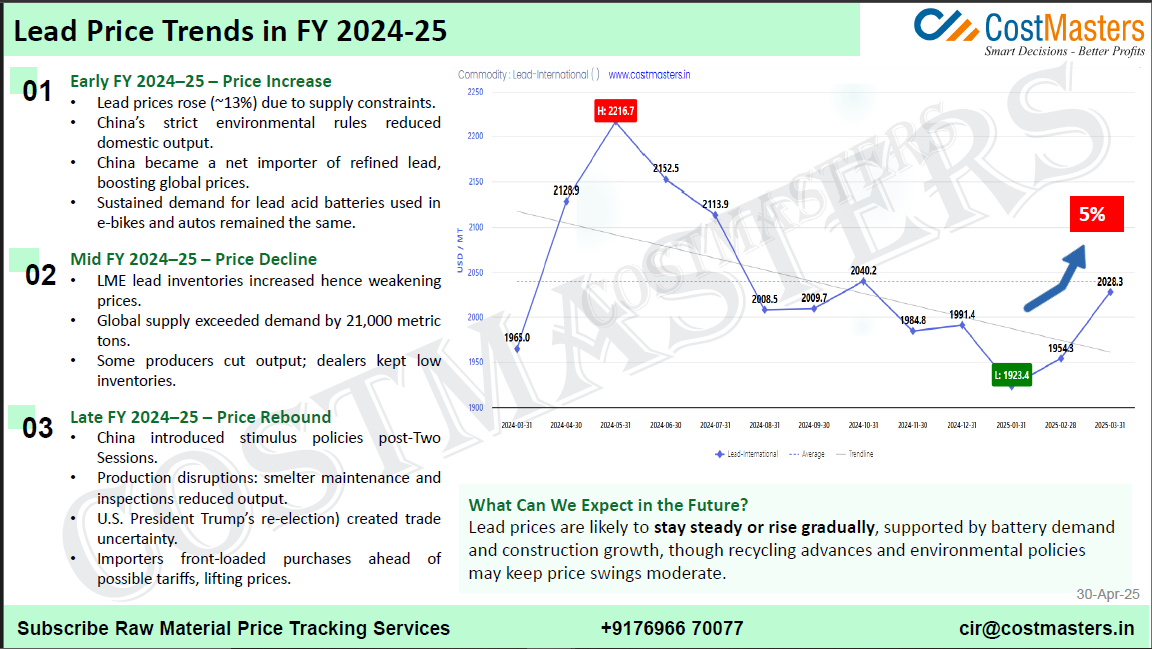
Early FY 2024 25 Price Increase
The fiscal year began with a significant surge in lead prices—around 13%, driven primarily by supply constraints. Several key developments fueled this uptick:
- China’s stringent environmental regulations led to reduced domestic lead production.
- As a result, China became a net importer of refined lead, placing upward pressure on global prices.
- Meanwhile, demand remained strong, particularly for lead-acid batteries used in electric bikes and automobiles.
These factors contributed to a price high of $2216.7/MT by mid-Q1 FY 2024–25.
Mid FY 2024–25 – Price Decline
The middle of the fiscal year saw a reversal in price trends. A mix of increased inventory and oversupply pushed prices down:
- LME inventories of lead grew, signaling a weaker market.
- Global supply exceeded demand by over 21,000 metric tons.
- Some producers scaled back output, while many dealers kept low inventories due to uncertainty.
By the end of this period, lead prices dropped to $1923.4/MT, the lowest of the fiscal year.
Late FY 2024–25 – Price Rebound
As the year closed, lead prices began to rebound, climbing roughly 5%. Several global and domestic developments contributed to the recovery:
- China introduced economic stimulus post-Two Sessions to boost industrial activity.
- Production disruptions—caused by smelter maintenance and regulatory inspections—further constrained supply.
- Trade tensions rose again following U.S. President Trump’s re-election, creating uncertainty in global markets.
- Importers front-loaded their purchases in anticipation of tariffs, increasing short-term demand and lifting prices
What Can We Expect in the Future?
Looking ahead, lead prices are likely to stay steady or rise gradually. This outlook is supported by:
- Sustained battery demand and construction growth.
- Continued advancements in recycling technologies.
- Stricter environmental policies that may keep wild price swings in check.